- Research Services
- Capabilities
- About Us
- Resources
- Contact Us
The direct effect of ionizing radiation during radiation therapy damages the DNA, lipids, and proteins of cells (both cancerous and non-cancerous) in the GI tract. In the rodent models, proctitis is induced with either a single bolus of acute radiation, or 8 fractionated, smaller doses, directed at approximately the most distal 2 cm of the colon (a lead shield protects the remainder of the animal’s body). Animals are monitored daily and evaluated for overall health and survival in addition to diarrhea and bloody stool incidence. A major readout in the model is proctitis severity determined via longitudinal video endoscopic assessments over the course of the study. Peak disease differs based on the method of induction, with disease persisting through the final evaluation which typically includes histopathology.
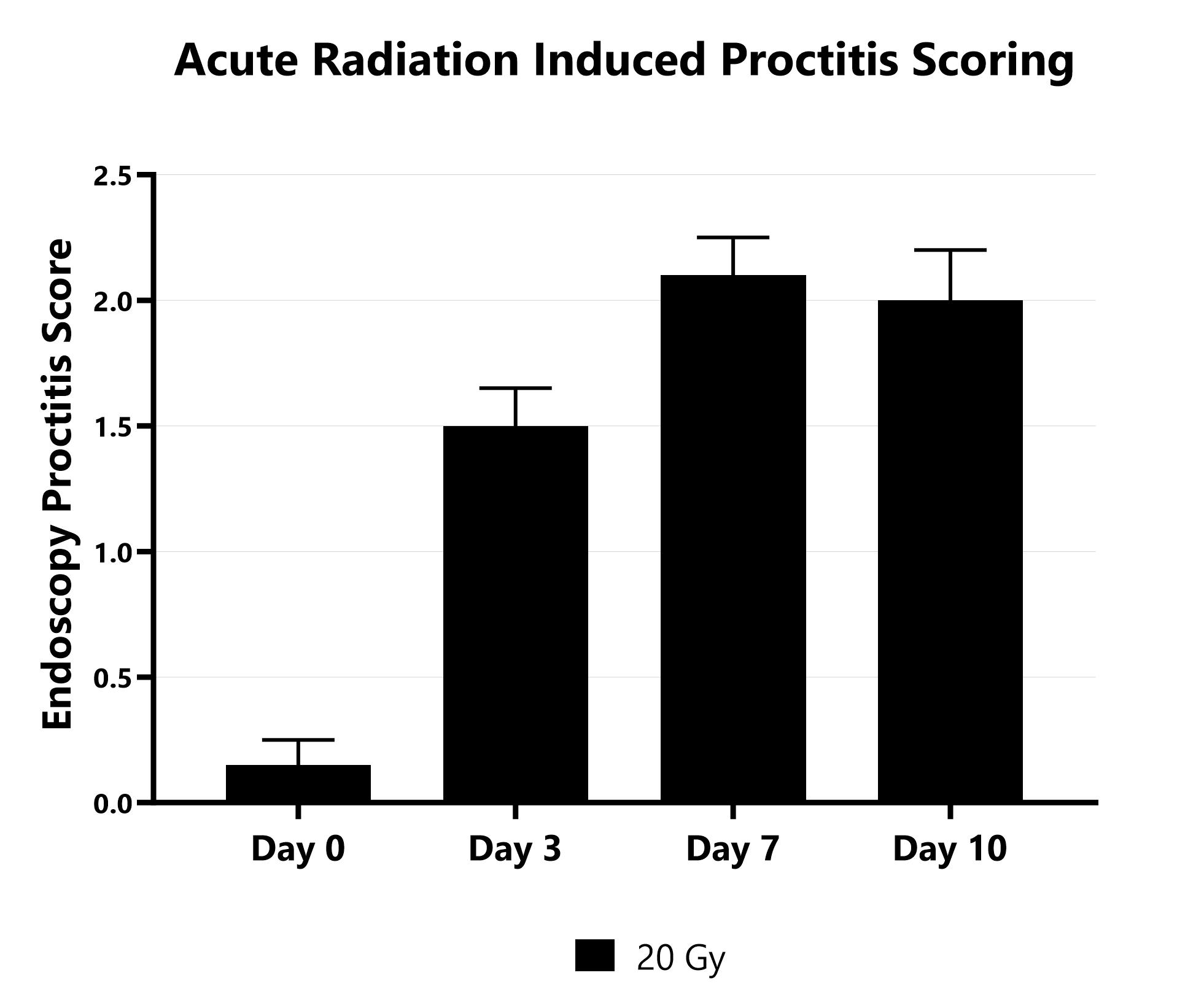
Proctitis severity is assessed longitudinally using video endoscopy at multiple timepoints during an acute radiation-induced proctitis study.
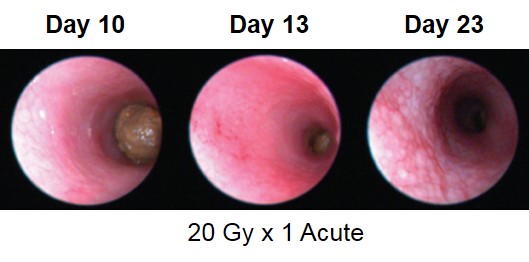
Proctitis severity is assessed longitudinally using video endoscopy at multiple timepoints during an acute radiation-induced proctitis study.
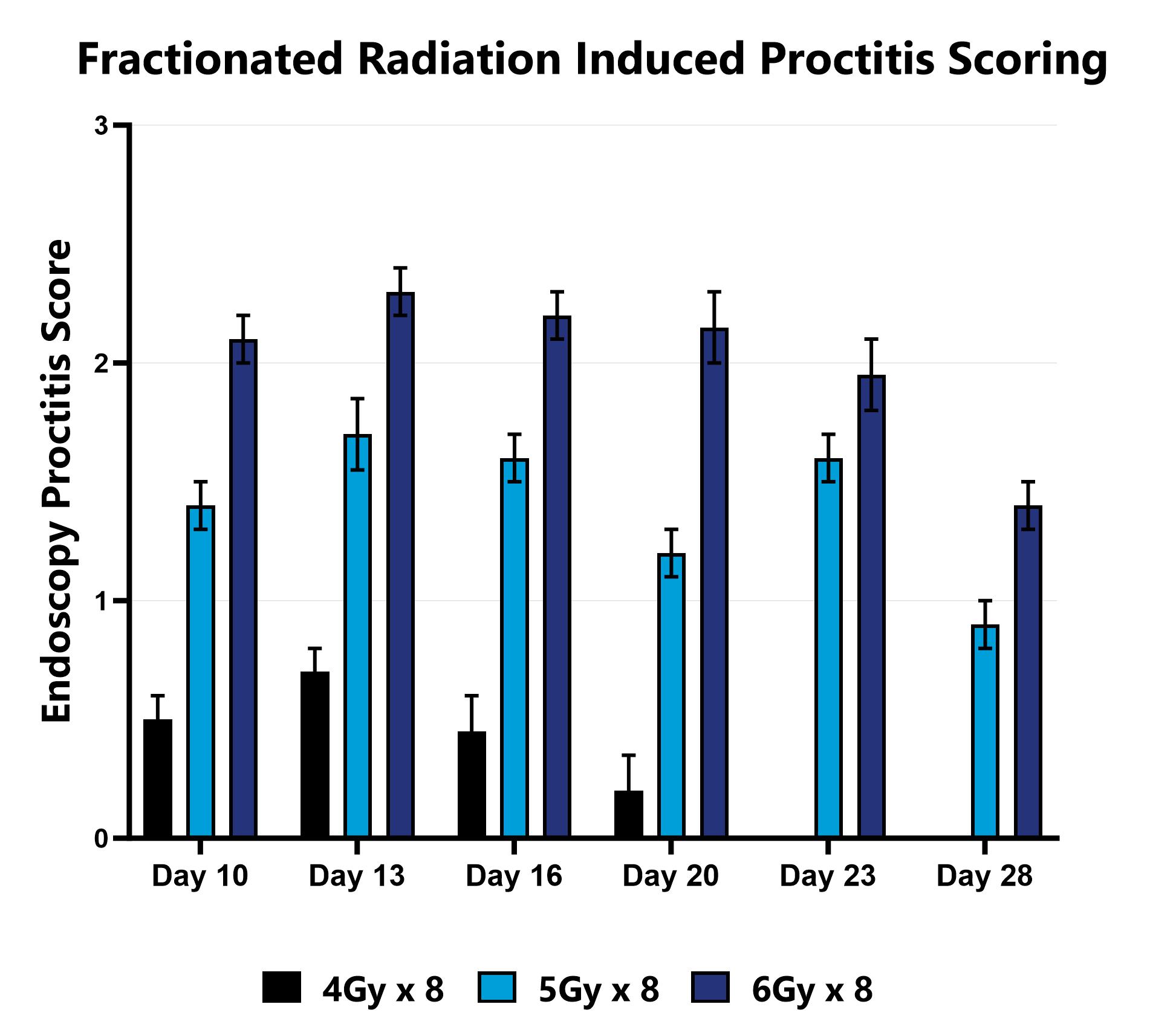
Proctitis severity is assessed longitudinally using video endoscopy at multiple timepoints during a fractionated radiation-induced proctitis study.
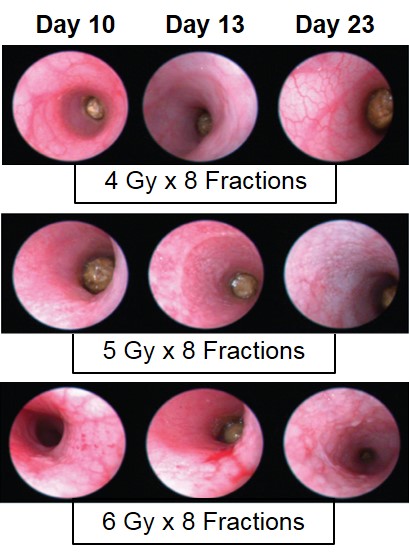
Proctitis severity is assessed longitudinally using video endoscopy at multiple timepoints during a fractionated radiation-induced proctitis study.
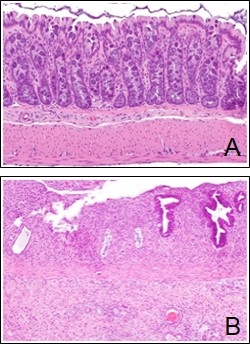
Following fractionated radiation treatment, rectal tissue is collected. (A) Photomicrograph showing histological appearance of normal rectal mucosa. (B) Photomicrograph showing histological appearance of inflamed rectal mucosa.
Your Message Was Submitted Successfully.